The Microsoft Access Linear Barcode Generator creates barcodes in Access Reports or Forms without requiring additional components such as fonts or DLLs. It utilizes data from the database to produce barcodes efficiently.
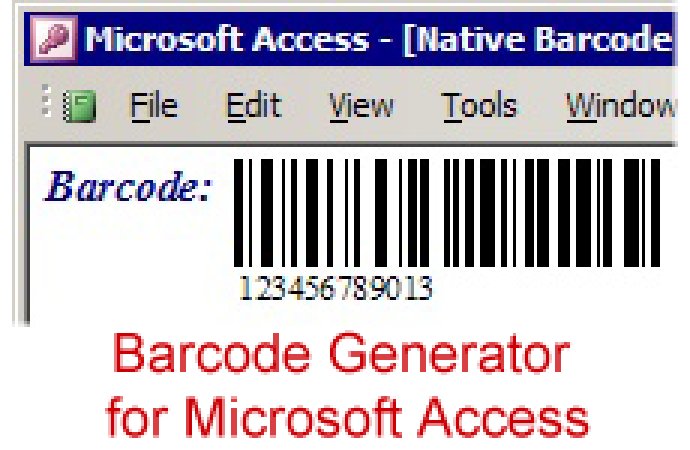
This product is fully compatible with Microsoft Access versions 2000 and up, and supports all languages and locales, including Double Byte versions of Windows used in countries such as China and Japan. Additionally, you can encode various functions into your barcodes, such as returns and tabs, which allow for output into multiple fields on scanning.
The Linear Barcode Generator for Access is available in several versions to meet your specific needs. This version supports Code 128, GS1-128, Code 39, Code 93, Codabar, Interleaved 2 of 5, MSI, USPS Intelligent Mail (IMb), Postnet and Planet, providing you with a range of options for your barcode generation.
IDAutomation offers Single and Multi-user licenses, as well as Developer License versions for commercial use, use in ERP/server environments, or in bundling with custom applications. Developer License versions also include complete source code, providing you with the flexibility to customize the product to meet your specific requirements.
Other features of the Microsoft Access Linear Barcode Generator include multiple locale compatibility with all languages and locales, including Double Byte versions of Windows, two wide-to-narrow ratios with ratios of 2:1 and 3:1 for Code 39, Interleaved 2 of 5, Codabar, and MSI, as well as easy function encoding capability for functions recording such as returns and tabs in Code 128.
Overall, the Microsoft Access Linear Barcode Generator is an excellent choice for anyone looking to create high-quality barcodes quickly and easily. With its robust set of features, compatibility with various locales and symbologies, and flexible licensing options, this product is sure to meet your needs.
Version 19.09: Added the ability to generate barcodes on a form in addition to reports to all symbologies except DataBar and USPS IMb.